Northrop/McDonnell Douglas YF-23 Black Widow II
 The Northrop/McDonnell Douglas YF-23 Black Widow II was a prototype fighter aircraft designed for the United States Air Force. It was passed over in favor of the YF-22 that has entered production as the F-22 Raptor.
The Northrop/McDonnell Douglas YF-23 Black Widow II was a prototype fighter aircraft designed for the United States Air Force. It was passed over in favor of the YF-22 that has entered production as the F-22 Raptor.
The YF-22 and YF-23 were competing in the USAF's Advanced Tactical Fighter program. Conceived in the early 1980s, to specify a replacement for the F-15 Eagle, contracts for the two most promising designs were awarded in 1986, with the YF-23 delivered in 1989 and the evaluation concluded in 1991.
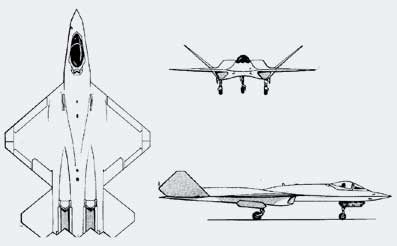
The YF-23 was designed with stealth as a high priority and was a highly unconventional-looking aircraft with diamond-shaped wings and a V-tail. The YF-23A met USAF requirements for survivability, supersonic cruise, stealth, and ease of maintenance. However, the YF-22A was more maneuverable than the YF-23A and won the competition in April 1991.
Although the precise results of the evaluation are not yet public knowledge, it is often claimed that the YF-23 was faster and stealthier than its competitor, but the USAF chose the YF-22 due to ease of production, maintenance, and potential for future development, as well as its relatively lower production cost. On the other hand, some say that the YF-22 was chosen for its superior subsonic maneuverability due to thrust vectoring. Others point out the YF-23's comparatively flawed weapons release mechanism wherein missiles are stacked on racks, and a weapons jam of a lower-positioned missile could prevent the firing of the missile above it.
Two aircraft were built. After losing the competition, both YF-23 prototypes were transferred from Northrop to NASA's Dryden Flight Center, at Edwards AFB, California.
Aircraft PAV-2 is now an exhibit at the Western Museum of Flight in Hawthorne, California and PAV-1 was recently moved to the National Museum of the United States Air Force, where it sits along side the Boeing X-32 in one of the Museum's restoration hangars awaiting restoration for display.
In late 2004, Northrop Grumman proposed a YF-23 based design for the USAF's interim bomber requirement, a role for which the FB-22 and B-1R are also competing. The interim bomber requirement has since been cancelled in favor of a more long-term, permament bomber replacement requirement; however, the same YF-23-derived design will likely be adapted to fulfill this role as well.
Specifications
Length: 67 ft 5 in (20.60 m)
Wingspan: 43 ft 7 in (13.30 m)
Height: 13 ft 11 in (4.30 m)
Wing area: 948 ft² (88m²)
Empty weight: 32,934 lb (14,970 kg)
Loaded weight: 51,320 lb (23,327 kg)
Max takeoff weight: 64,000 lb (29,029 kg)
Powerplant:
2× General Electric YF120 or Pratt & Whitney YF119 turbofan, 35,000 lbf (277 kN)Performance:
Maximum speed: 1,400 mph (2,240 km/h)
Combat radius: 921 miles (1,474 km)
Service ceiling: 65,000 ft (19,800 m)
Wing loading: 54 lb/ft² (265 kg/m²)
Thrust/weight: 1.4
Armament:
1× 20 mm M61 Vulcan cannon
6× air-to-air missiles, including the AIM-120 AMRAAM and AIM-9 Sidewinder
Links:
www.fas.org
www.voodoo.cz
www.globalaircraft.org
www.dreamlandresort.com
(Adapted from http://www.wikipedia.org/ )
Labels: aircraft, aviation, dreamhost promocode, F-15 Eagle, F-22 Raptor, links, McDonnell Douglas, Northrop, stealth, supersonic cruise, thrust vectoring, V-tail, YF-22, YF-23 Black Widow



0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< Home