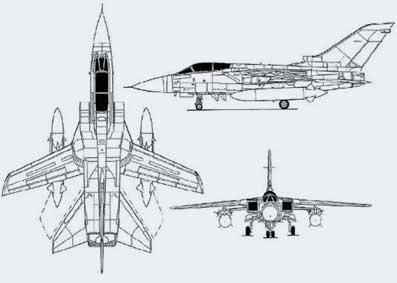
Panavia Tornado IDS

The Panavia Tornado is a family of twin-engine fighters, which was jointly developed by the United Kingdom, Germany and Italy. There are three primary versions of the Tornado, the fighter-bomber Tornado IDS (Interdictor/Strike), the interceptor Tornado ADV (Air Defence Variant), and the suppression of enemy air defences Tornado ECR (Electronic Combat/Reconnasiance).
Developed and built by Panavia, a trination consortium consisting of British Aerospace, MBB of Germany, and Alenia Aeronautica of Italy, the Tornado first flew on August 14, 1974, and saw action with the RAF in Desert Storm.
Including all variants, 992 aircraft were built for the three partner nations and Saudi Arabia. Though still in service, plans are currently underway to replace the aircraft.
The Tornado was originally designed as a low-level supersonic ground attack bomber, capable of taking off and landing in short distances. This requires good high-speed and low-speed flying characteristics.
When the wings are swept back, the Tornado increases its high-speed low-level capability by reducing drag. When sweeping, the wings partially slide into the fuselage, reducing the exposed wing area. This gives the aircraft a low gust response in turbulent low-level winds. This not only makes flight much more comfortable for the aircrew but importantly it makes the aircraft a more stable platform from which to aim and deliver unguided weapons at low-level.
With the wings swept fully forwards the Tornado GR4 generates greater lift because of the increased exposed wing area and the utility of full-span flaps and slats. This gives greater lift at lower speeds, reducing the minimum landing speed required and therefore shorter landing distances.
There are three primary subvariants, the Interdictor/Strike (IDS), the Air Defence Variant (ADV), and the Electronic Combat/Reconnasiance (ECR), with 80% commonality between the airframes.
The Tornado IDS is operated by Germany, Italy, Saudi Arabia and the United Kingdom. It is one of the world's most sophisticated and capable interdiction and attack aircraft, with a large payload, long range and high survivability.
The Tornado was cleared to carry almost all the air-launched weapons in the NATO inventory, including cluster bombs, anti-runway munitions, and nuclear weapons. The aircraft also has a limited air-to-air capability with Sidewinder AAMs.
The Tornado was designed for ultra-low level penetration strikes on Warsaw Pact targets in Europe using both conventional and tactical nuclear weapons, e.g WE.177. However, the end of the Cold War precluded it from ever seeing that use. A major feature of the Tornado GR.1 was its terrain-following radar, which allowed all-weather hands-off low-level flight, but current doctrine eschews extreme low-level flight and relies on inertial navigation with GPS updates rather than TFS.
Its actual combat debut came in 1991 in the Gulf War. Nearly 60 GR1s were deployed by the United Kingdom to bases in Bahrain and Saudi Arabia. The main initial task of the GR.1s was to use the JP233 runway denial weapon on Iraqi airfields. Flying a supersonic speeds at 50 to 100 feet above the ground proved costly for the Royal Air Force, as six aircraft were lost to Iraqi defences.
On September 25, 1985, UK and Saudi Arabia signed the Al Yamamah I contract including, amongst other things, the sale of 48 IDS and 24 ADV model Tornados. The first flight of a RSAF Tornado IDS was on March 26, 1986, and the first Saudi ADV was delivered on February 9, 1989.
Specifications (Tornado IDS GR.4)
General characteristics:
Length: 16.72 m (54 ft 10 in)
Wingspan: 13.91 m at 25° wing sweep, 8.60 m at 67° wing sweep (45.6 ft / 28.2 ft)
Height: 5.95 m (19.5 ft)
Wing area: 26.6 m² (286 ft²)
Empty weight: 13,890kg (31,620lb)
Max takeoff weight: 28,000 kg (61,700 lb)
Powerplant:
2× Turbo-Union RB199-34R Mk 103 afterburning turbofans, 43.8 kN dry, 76.8 kN afterburning (9,850 lbf / 17,270 lbf) each
Performance:
Maximum speed: Mach 2.27, 2,338 km/h (1,452 mph)
Range: 1,390 km typical combat, 3,890 km ferry with four external drop tanks (870 mi / 2,420 mi)
Service ceiling: 15,240 m (50,000 ft)
Rate of climb: 76.7 m/s (15,100 ft/min)
Armament:
1x 27 mm Mauser BK-27 cannon with 180 rounds
ECM pods, two AIM-9 Sidewinder or ASRAAM self-defence missiles.
Links:
www.tornado-data.com
www.airforce-technology.com
www.aeroflight.co.uk
www.airliners.net
Vídeo:
Vídeo #1
Vídeo #2
Vídeo #3
(Adapted from http://www.wikipedia.org/ )
Labels: AIM-9, aircraft, ALARM, Alenia, ASRAAM, Brimstone, British Aerospace, dreamhost promocode, JP233, Kormoran, links, Mauser, Maverick, MBB, Panavia Tornado, Paveway, RB199, Taurus





0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< Home