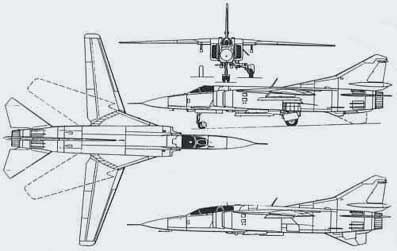
General Dynamics F-111
 In June 1960 the USAF issued a specification for a long-range interdiction/strike aircraft able to penetrate Soviet air defenses at very low altitudes and very high speeds to deliver tactical nuclear weapons against crucial Soviet targets like airfields and supply depots. Included in the specification were a low-level speed of Mach 1.2, a high-altitude speed of Mach 2.5, a combat radius of 890 mi (1,430 km), good short-field performance, and a ferry range long enough to reach Europe unrefueled.
In June 1960 the USAF issued a specification for a long-range interdiction/strike aircraft able to penetrate Soviet air defenses at very low altitudes and very high speeds to deliver tactical nuclear weapons against crucial Soviet targets like airfields and supply depots. Included in the specification were a low-level speed of Mach 1.2, a high-altitude speed of Mach 2.5, a combat radius of 890 mi (1,430 km), good short-field performance, and a ferry range long enough to reach Europe unrefueled.The U.S. Navy, meanwhile, had since 1957 been searching for a long-range, high-endurance interceptor to defend its carrier groups against the new generation of Soviet jet bombers, which by then were being armed with huge anti-ship missiles with nuclear warheads.
 The program was dubbed TFX (Tactical Fighter Experimental). The TFX design eventually emerged as an aircraft in the 20-ton (empty) class with a maximum take-off weight of almost 50 tons. It had been intended to use titanium for large portions of the airframe to save weight, but this proved prohibitively expensive. The TFX was powered by two afterburning Pratt & Whitney TF30-P-100 turbofans in the 80 kN class. The shoulder-mounted wings were attached to a pair of giant pivots, allowing it to take off, land, and loiter with a modest 16° sweep (for maximum lift and minimum landing speed), cruise at high subsonic speeds with a 35° sweep, or sweep back to a 72.5° maximum for fast supersonic dashes at more than Mach 2. Despite its high maximum speed, its modest thrust fraction (thrust-to-weight ratio) made early versions somewhat underpowered, exacerbated by compressor stalls and other engine problems that forced a hasty redesign of the engine inlets.
The program was dubbed TFX (Tactical Fighter Experimental). The TFX design eventually emerged as an aircraft in the 20-ton (empty) class with a maximum take-off weight of almost 50 tons. It had been intended to use titanium for large portions of the airframe to save weight, but this proved prohibitively expensive. The TFX was powered by two afterburning Pratt & Whitney TF30-P-100 turbofans in the 80 kN class. The shoulder-mounted wings were attached to a pair of giant pivots, allowing it to take off, land, and loiter with a modest 16° sweep (for maximum lift and minimum landing speed), cruise at high subsonic speeds with a 35° sweep, or sweep back to a 72.5° maximum for fast supersonic dashes at more than Mach 2. Despite its high maximum speed, its modest thrust fraction (thrust-to-weight ratio) made early versions somewhat underpowered, exacerbated by compressor stalls and other engine problems that forced a hasty redesign of the engine inlets.First flight of the F-111A, as the USAF version was designated, was 21 December 1964, and entry into service with the USAF began 18 July 1967.
The Navy version, the F-111B (visually distinguishable from all other variants due to its noticeably shorter nose), was cancelled in December 1968 to be replaced by the F-14 Tomcat, but other F-111 variants went on to serve with the USAF through the mid-1990s, performing with distinction in the 1991 Gulf War. Although the United Kingdom had expressed interest in the program in 1965 in preference to the home grown BAC TSR-2, the British order for the F-111 was cancelled, and the F-111's only export customer was the Royal Australian Air Force.
Currently the Royal Australian Air Force is the only operator of the F-111 and continues to upgrade the aircraft with modern avionics as well as modern weapon systems.
 To replace the elderly and obsolescent Douglas EB-66, in 1972 the USAF contracted Grumman to convert some existing F-111As into electronic warfare/ECM aircraft. The Air Force had considered the Navy Grumman EA-6B Prowler, but was reluctant to adopt a Navy aircraft.
To replace the elderly and obsolescent Douglas EB-66, in 1972 the USAF contracted Grumman to convert some existing F-111As into electronic warfare/ECM aircraft. The Air Force had considered the Navy Grumman EA-6B Prowler, but was reluctant to adopt a Navy aircraft.A contract to develop the EF-111A was awarded to Grumman in 1974, modifying existing -A airframes. The first fully equipped model flew on 10 March 1977,known then as the "Electric Fox", and deliveries to combat units began in 1981. A total of 42 conversions were completed, the last delivered by the end of 1985. The EF-111A received the official popular name Raven, although in service it acquired the nickname "Spark 'Vark".
 Specifications (F-111)
Specifications (F-111)General characteristics
Crew: Two (pilot and weapons system operator)
Length: 73.5 ft (22.4 m)
Wingspan: 63.0 ft spread, 32.0 ft swept (19.2 m / 9.74 m)
Height: 17.13 ft (5.22 m)
Wing area: 657.4 ft² spread, 525 ft² swept (61.07 m² / 48.77 m²)
Empty weight: 47,481 lb (21,537 kg)
Loaded weight: 82,843 lb (37,577 kg)
Maximum gross takeoff weight: 98,979 lb (44,896 kg)
Powerplant:
2× Pratt & Whitney TF30-P-100 turbofans with afterburner, 25,100 lbf (111.7 kN) each
Performance:
Maximum speed: Mach 2.5, 1,855 mph (2,985 km/h)
Range: 1,330 mi combat, 3,220 mi ferry (2,140 km / 5,185 km)
Service ceiling: 56,650 ft (17,270 m)
Rate of climb: 25,890 ft/min (131.5 m/s)
Armament:
1× M61 Vulcan 20 mm gatling cannon (seldom fitted)
31,500 lb (14,300 kg) of ordnance
Links:
RAAF
http://www.f-111.net/
http://www.fas.org/man/dod-101/sys/ac/f-111.htm
http://www.aerospaceweb.org/aircraft/bomber/f111/
Video: F-111
(Adapted from http://www.wikipedia.org/)