Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-23 “Flogger”
 The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-23 (NATO reporting name 'Flogger') is a variable geometry, swept-wing fighter aircraft, originally built by the Mikoyan-Gurevich design.DevelopmentThe MiG-23's predecessor, the MiG-21 Fishbed, was fast and agile, but very limited in its operational capabilities.The MiG-23 was to be a heavier, more powerful machine designed to remedy these deficiencies, and, it was hoped, rival Western aircraft like the F-4 Phantom.
The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-23 (NATO reporting name 'Flogger') is a variable geometry, swept-wing fighter aircraft, originally built by the Mikoyan-Gurevich design.DevelopmentThe MiG-23's predecessor, the MiG-21 Fishbed, was fast and agile, but very limited in its operational capabilities.The MiG-23 was to be a heavier, more powerful machine designed to remedy these deficiencies, and, it was hoped, rival Western aircraft like the F-4 Phantom.  A major design consideration was take-off and landing performance. The Soviet Air Force demanded that the new aircraft have a much shorter take-off run. Also, low-level speed and handling was to be improved over MiG-21The second prototype, known as 23-11, featured variable-geometry wings which could be set to angles of 16, 45 and 72 degrees, and it was clearly more promising. The order to start series production of the MiG-23 was given in December 1967.
A major design consideration was take-off and landing performance. The Soviet Air Force demanded that the new aircraft have a much shorter take-off run. Also, low-level speed and handling was to be improved over MiG-21The second prototype, known as 23-11, featured variable-geometry wings which could be set to angles of 16, 45 and 72 degrees, and it was clearly more promising. The order to start series production of the MiG-23 was given in December 1967.  Service careerThe first MiG-23s to see combat were export variants with many limitations. For example, MiG-23MS lacked such a basic system as radar warning receiver. In addition, compared to MiG-21, the aircraft was mechanically complex and expensive. In the 1980s, an improved MiG-23ML was widely exported, which performed better and was met with more enthusiasm by its users.It is known that some number of air victories were scored by MiG-23s in the Iran-Iraq War. Cuban MiG-23MLs and South African Mirage F.1s had several encounters during Angolan War. Soviet MiG-23MLDs and Pakistani F-16s clashed a few times during Afghan-Soviet War; one F-16 was reportedly lost in a friendly fire incident (according to the Pakistanis), but Russian reports claim the F-16 was shot down by a MiG-23MLD.
Service careerThe first MiG-23s to see combat were export variants with many limitations. For example, MiG-23MS lacked such a basic system as radar warning receiver. In addition, compared to MiG-21, the aircraft was mechanically complex and expensive. In the 1980s, an improved MiG-23ML was widely exported, which performed better and was met with more enthusiasm by its users.It is known that some number of air victories were scored by MiG-23s in the Iran-Iraq War. Cuban MiG-23MLs and South African Mirage F.1s had several encounters during Angolan War. Soviet MiG-23MLDs and Pakistani F-16s clashed a few times during Afghan-Soviet War; one F-16 was reportedly lost in a friendly fire incident (according to the Pakistanis), but Russian reports claim the F-16 was shot down by a MiG-23MLD. Western pilots who flew the MiG-23 said its handling was similar to something between the F-4E and the Panavia Tornado in some parts of the flight envelope, and more like the F-105 in others. Soviet manuals considered the MiG-23MLD's performance and handling superior to that of the F-4E and, in some parts of the flight envelope, better than the F-16A's, but admitted that the F-15 has an overwhelming superiority over the MiG-23 family. The Israelis tested the MiG-23 and found that it had better acceleration than the F-16 and F-18. Overall, the MiG-23 represents the final incarnation of the late 1960s fighter technology which, despite being developed close to its full potential, was quickly overtaken by next generation. The MiG-23's closest contemporaries are perhaps the Mirage F.1 and Saab Viggen, which ended up with fairly similar careers.
Western pilots who flew the MiG-23 said its handling was similar to something between the F-4E and the Panavia Tornado in some parts of the flight envelope, and more like the F-105 in others. Soviet manuals considered the MiG-23MLD's performance and handling superior to that of the F-4E and, in some parts of the flight envelope, better than the F-16A's, but admitted that the F-15 has an overwhelming superiority over the MiG-23 family. The Israelis tested the MiG-23 and found that it had better acceleration than the F-16 and F-18. Overall, the MiG-23 represents the final incarnation of the late 1960s fighter technology which, despite being developed close to its full potential, was quickly overtaken by next generation. The MiG-23's closest contemporaries are perhaps the Mirage F.1 and Saab Viggen, which ended up with fairly similar careers.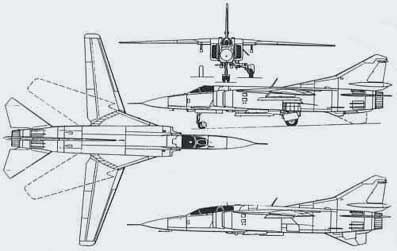
Specifications (MiG-23MLD Flogger-K)
General characteristics
Crew: One
Length: 16.70 m (56 ft 9.5)
Wingspan: Spread, 13.97 m (45 ft 10 in)
Height: 4.82 m (15 ft 9.75 in)
Wing area: 37.35 m² spread, 34.16 m² swept (402.05 ft² / 367.71 ft²)
Empty weight: 9,595 kg (21,153 lb)
Loaded weight: 15,700 kg (34,612 lb)
Maximum gross takeoff weight: 18,030 kg (39,749 lb)
Powerplant: 1× Khatchaturov R-35-300 afterburning turbojet, 83.6 kN dry, 127 kN afterburning (18,850 lbf / 28,700 lbf)
Performance:
Maximum speed: Mach 2.35, 2,500 km/h at altitude; Mach 1.14, 1,350 km/h at sea level (1,553 mph / 840 mph)
Range: 1,150 km with six AAMs combat, 2,820 km ferry (570 mi / 1,750 mi)
Service ceiling: 18,500 m (60,695 ft)
Rate of climb: 240 m/s (47,245 ft/min)
Wing loading: 575 kg/m² (118 lb/ft²)
Thrust/weight: 0.88:1
Armament:
1x Gryazev-Shipunov GSh-23L 23 mm cannon with 200 rounds Two fuselage, two wing glove, and two wing pylons for up to 3,000 kg (6,614 lb) of stores, including: R-23/24 (AA-7 Apex) R-60 (AA-8 Aphid) also, upgraded aircraft may carry: R-27 (AA-10 Alamo) R-73 (AA-11 Archer) R-77 (AA-12 Adder)
Links:
http://www.fas.org/nuke/guide/russia/airdef/mig-23.htm
http://www.todo-aviones.com.ar/rusos/mig23/gal_mig23.html
http://www.defencetalk.com/air_systems/fighters/mig-23_flogger.html
(Adapted from http://www.wikipedia.org/)



0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< Home